Links
Two new key genes for anthocyanin synthesis have been discovered
Recently, the innovative team for functional components and biosynthesis of tobacco of Tobacco Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences identified two key regulatory genes involved in anthocyanin synthesis from Chinese wild rice and elucidated their mechanisms of action in the biological enhancement of anthocyanin in rice seeds through functional verification of rice transformation. The relevant research results were published in Food Chemistry.
Compared with common colorless rice, Chinese wild rice contains more abundant functional components such as flavonoids and anthocyanins, and has excellent antioxidant properties. Exploring the key genes involved in anthocyanin synthesis in Chinese wild rice from the perspective of biological enhancement, and analyzing their mechanisms in nutrient enhancement of staple foods such as rice, is of great significance for breeding functional rice varieties and maintaining people’s nutritional health.
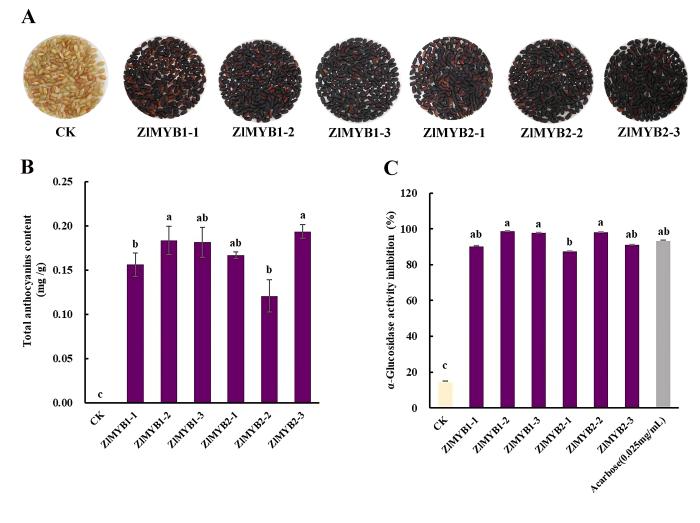
This study cloned two key regulatory genes for anthocyanin synthesis, ZlMYB1 and ZlMYB2, whose overexpression could significantly enhance the total anthocyanin content, antioxidant activity, and enzyme inhibition of α-glucosidase in rice seeds. Through the analysis of flavonoid metabolome, transcriptome, gene expression, and enzyme activity, it was determined that these two genes can activate the expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis structural genes F3’H and UFGT. This study proposes the idea of using genes from miscellaneous grains to achieve nutritional enhancement of staple foods, and also provides an example for the exploration of functional component gene resources in miscellaneous grains and their utilization in nutritional enhancement of staple foods.
This work was funded by the Youth Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province.
linkage: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140670